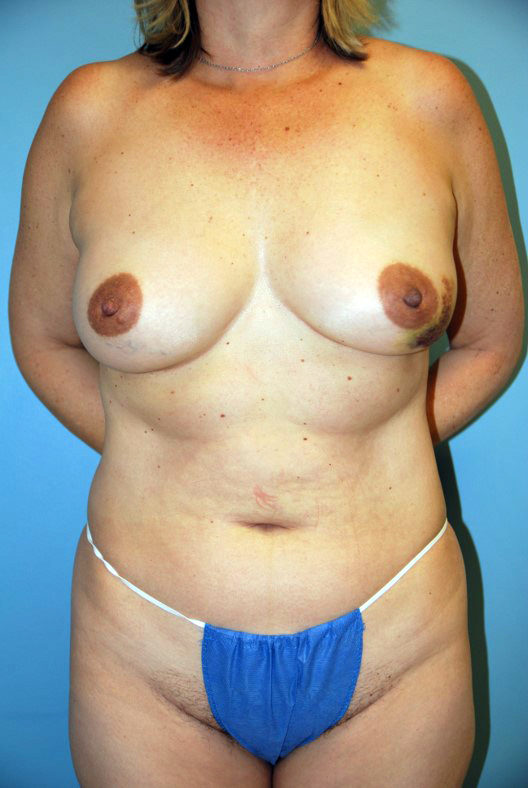
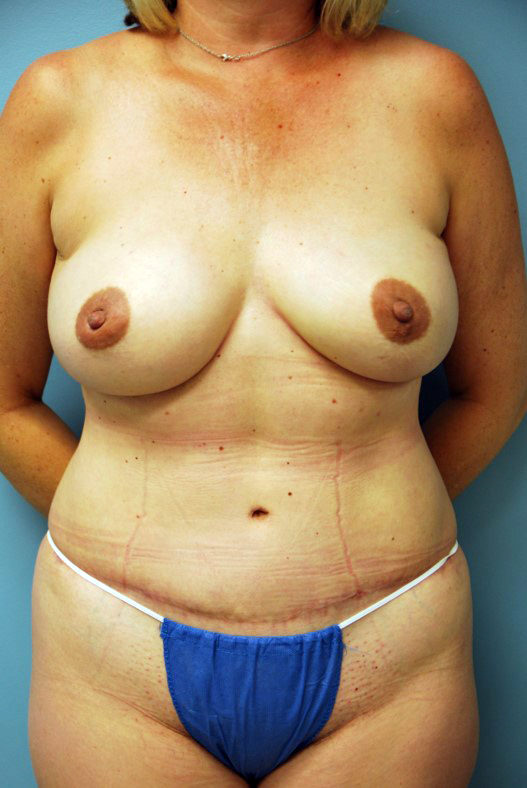
restoreDIEP Flap
restoreDIEP Flap
Procedure
DIEP/SIEA Free Flap Reconstruction: Using Your Own Tissue
This type of surgery involves reconstructing the breast with the patient’s own tissue (skin, fat). This tissue is taken from another area of the body that has excess tissue, such as the abdomen, thigh, buttock, or back, and this tissue is then transferred and molded to create a breast.
DIEP and SIEA breast reconstruction are autologous free flaps. A free flap is a type of tissue transfer that involves completely disconnecting the tissue from its original location and blood supply and moving the tissue to a new location on the body, where the blood supply is reconnected. This advanced procedure is made possible through the use of microsurgical technique and surgical expertise.
The DIEP flap (Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator) and the SIEA (Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator) flap are both advanced microsurgical free flaps that use the patient’s excess abdominal skin and fat to reconstruct the breast.
The Difference Between the DIEP and SIEA flap
The lower abdomen is the donor site for the free tissue transfer for both flaps. The difference between the two flaps is the choice of blood vessels that are used to nourish the flap tissue.
- In DIEP flap breast reconstruction, the blood vessels are contained in the abdominal rectus muscle and advanced microsurgical techniques are used to safely separate the artery and vein from the muscle while preserving the muscular integrity, or function
- In SIEA flap reconstruction, the blood vessels are more superficial and they travel in the fatty layer of the abdominal tissue. Therefore, less dissection is required than in the DIEP flap
Although the SIEA flap requires less dissection, the superficial vessels may be absent in some patients. Therefore, the decision as to which flap is performed is made during the reconstructive surgery, based on the individual patient’s anatomy.
Procedure Details
In the DIEP/SIEA flap the excess lower abdominal tissue is completely detached from the abdomen and re-attached to the small blood vessels in the breast area, resulting in a microsurgical tissue transfer. These tiny blood vessels require the surgeon to use a microscope to connect them together. Once this is complete, the blood flow to the tissue is restored. The tissue is then shaped to fit the mastectomy defect and a small skin patch is left. The skin patch from the abdomen maybe used during a second stage procedure to reconstruct the nipple. For patients who underwent a complete mastectomy, the abdominal skin is used to replace the missing breast skin.
The skill of the surgeon in breast flap reconstruction is considerably more demanding than earlier methods of breast reconstruction. Previous methods of breast reconstruction involved muscle removal, which made these procedures easier and faster, but came with considerable negative consequences, such as abdominal bulging and abdominal muscle weakness. Unlike the TRAM flap, which is an abdominal flap that removes muscle, the DIEP free flap spares the abdominal muscle and transfers to the breast only fatty tissue and skin. Compared to earlier techniques, the DIEP free flap operation can be lengthy due to the precise nature of this microsurgical procedure. However, the surgical effort is rewarded by excellent cosmetic results, improved abdominal donor site aesthetics, and preservation of abdominal muscle function. The procedure is also less invasive, resulting in less pain and faster recovery, as compared to the earlier techniques.
Additionally, for both the DIEP and SIEA free flaps, we can now offer routine re-innervations where nerves are connected to facilitate gradual return of sensation in the reconstructed breast.
The Incision
The DIEP/SIEA flap operation leaves a horizontal scar on the lower abdomen, similar to that created in a cosmetic tummy tuck, resulting in a slimmer abdominal contour that is appreciated by most women.
An incision is made from hip to hip on the lower abdomen. Special attention is taken in the placement of the incision to ensure it can easily be hidden in a bikini. You will also have an incision on the breast. The location of the breast incision varies patient to patient. Factors to consider include the type of mastectomy the patient is having, the incision the general surgeon will be using to complete the mastectomy, and if the reconstruction is delayed the specific past surgical history.
Candidates
You may be a candidate for DIEP/SIEA breast reconstruction if:
- You are in good general health with an adequate amount of abdominal tissue
- You are scheduled to have a mastectomy due to a new breast cancer diagnosis or you are considering a prophylactic mastectomy
- You have had a previous mastectomy without breast reconstruction and would like to discuss delayed breast reconstruction options
- You desire a more natural looking and feeling breast reconstruction
- You are interested in the possibility to restore breast sensation after mastectomy
- You are interested in lymph node transfer with your breast reconstruction
- You had previous breast reconstruction with implants and have been experiencing complications such as infection or capsular contracture
Things to consider:
- This is a more technical, and therefore, lengthier and more intensive procedure than other types of breast reconstruction. This will result in a longer surgery and a hospital stay of 3-4 days
- You will need to be in good general health and will be required to have a cardiac clearance with a stress test prior to being cleared for this procedure
- You will need support at home to help during your recovery process
- This is a two stage procedure with the second stage of the procedure occurring no earlier than 3-4 months after the first stage.
- The first stage of the procedure focuses on safely transferring the tissue from the abdomen to the breast
- The second stage of the procedure focuses on refining the breast shape and volume, addresses symmetry between the breasts, and further contours the abdomen
- All breast reconstruction and breast symmetry procedures, following a mastectomy, are covered by insurance, as legislated in 1998.

Benefits
In the hands of a specialized surgeon who performs microsurgical procedures on a regular basis however, the DIEP Flap procedure proves to be more advantageous to women facing breast reconstruction after mastectomy. The more advanced DIEP surgery is a complex procedure and ultimately more technically demanding of the surgeon, with reconstruction on one breast lasting anywhere from four to six hours and six to eight hours for both breasts. Nevertheless, the results provide patients with a significantly more elegant solution in terms of utilizing abdominal tissue. Unlike the TRAM Flap, which requires the removal of abdominal muscle and fascia, DIEP surgery lessens the surgical burden on the donor tissue site by harvesting only abdominal skin and fat without the need to remove any of the rectus abdominis muscle. As a result of using this sophisticated muscle-preserving technique as opposed to the TRAM Flap, patients experience less postoperative pain and retain abdominal wall strength, which is important for reducing the risk of post-surgical complications such as hernias or bulges.
The DIEP flap procedure results in a more natural result than that of an implant, as these techniques utilize the patient’s own tissue. However, the preservation of abdominal muscle and shorter hospital stays associated with the DIEP Flap ultimately make this technique more favorable for women seeking breast reconstruction after mastectomy. It is Dr. Spiegel’s philosophy that almost all patients who qualify for the TRAM Flap are candidates for the improved DIEP surgery as well. She strongly believes in the value of preserving the abdominal muscle to maintain trunk flexion function and reduce the risk of hernia formation. In addition she is committed to ensuring that the recovery phase for her patients is as painless and unproblematic as possible. For this reason she focuses her clinical expertise on advanced microsurgery and more sophisticated muscle-preserving perforator flaps.
There are multiple benefits of the DIEP and SIEA procedures including:
- Natural feel and appearance of the breast
- This procedure uses your abdominal tissue to reconstruct the breasts, creating a more natural look and feel of the breasts, that will change with you as your body changes, i.e. aging and weight loss/gain.
- Flatter, contoured, abdomen
- This procedure uses your excess abdominal tissue to reconstruct the breast, and as a result also achieves a flatter more aesthetically pleasing abdomen
- Although this procedure uses your abdominal tissue (skin and fat), unlike the TRAM flap, it keeps your abdominal muscle intact. This allows for full function of the abdominal muscle after the procedure.
- Ability to correct deformity from a prior procedures
- Skin can be transferred with the fatty tissue of the abdomen to correct a deformity that was created by a previous procedure
- Improved breast sensation
- After a mastectomy, the sensation of the breast changes due to sensory nerves that maybe cut or removed with the breast tissue. During DIEP or SIEA reconstruction, a nerve can be transferred and connected in the breast to improve sensation
- Improved Lymphedema
- A common complication that can occur with breast cancer treatment is lymphedema. During DIEP or SIEA reconstruction, it is possible to transfer a lymph node with the abdominal tissue. This allows for both breast reconstruction and treatment of lymphedema within the same procedure.

Recovery
After your breast reconstruction, your breast incisions will be covered with Dermabond (surgical glue) and your abdominal incision will be covered with a special surgical tape to protect the incision. You will not be required to do any wound care or dressing changes at home. Surgical drains will be placed, typically two drains are placed to each operated breast, and a total of two drains are placed to the abdomen (one on each side) You will go home with your drains and you will be taught how to care for the drains at home. All drains are typically removed within 2-3 weeks.
After a DIEP/SIEA flap, patients are recovering from both breast reconstruction and a “tummy tuck”. In order to protect the abdominal incision, there are special abdominal precautions while recovery. Patients must walk flexed at the hips and also must sleep in a recliner chair, in order to take tension off of the abdominal incision. Typically, these abdominal precautions are continued for approximately 4 weeks, or until the tension on the abdominal incision decreases.
As with any surgery, some swelling, bruising, and soreness are to be expected at first. You will be administered pain medication to help control any post-op discomfort. This tenderness and swelling should begin to subside after a few days. The majority of swelling should begin to resolve after a few weeks.
Patients have a relatively short hospital stay of 3-4 days and can return to normal daily activities at approximately four weeks. Most patients are able to resume all activities without restrictions, including lifting at 2-3 months. For a detailed layout of what to expect after your DIEP/SIEA flap procedure please click the Post Op link.

Results
The reconstructed breasts will be natural in look and feel. This breast reconstruction has the added benefit of removing excess abdominal tissue and achieving a slimmer and more contoured abdomen. The DIEP/SIEA procedure also offers the opportunity to combine other procedures that may result in improved breast sensation and lymphedema. The fatty tissue of the abdomen, that is transferred to reconstruct the breasts, will change with you as your body changes resulting in long lasting natural results. Be sure to keep all follow-up evaluations with Dr. Spiegel, and do not hesitate to contact her if you notice any changes or have any concerns.